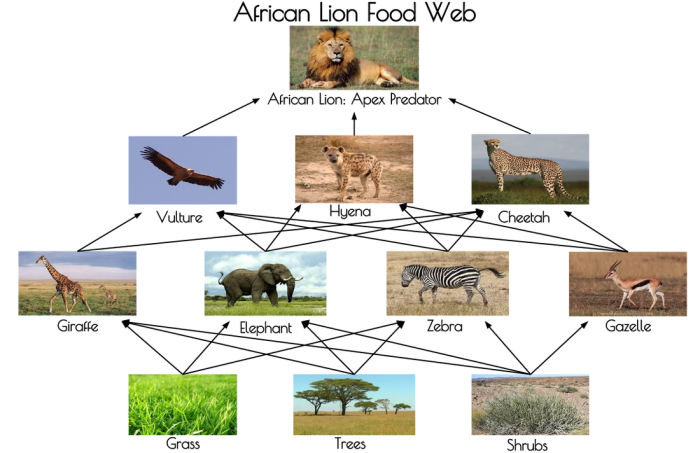
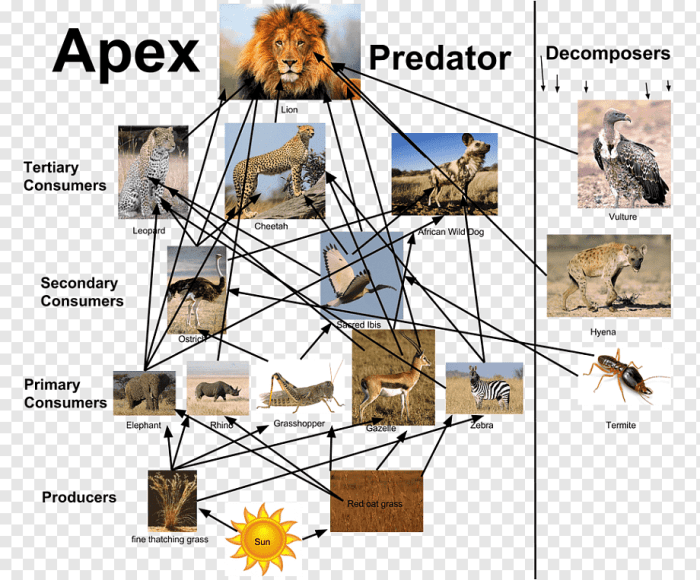
Embark on an educational journey with our comprehensive lion king food web worksheet answers, meticulously crafted to unravel the complexities of this captivating ecosystem. This guide delves into the intricate relationships between organisms, revealing the delicate balance that sustains the African savanna.
Our exploration will delve into the concepts of food chains and food webs, shedding light on the interconnectedness of species. We will identify the various trophic levels within the lion king food web, understanding their significance in the flow of energy and nutrients.
Moreover, we will uncover the diverse interactions between organisms, from predator-prey dynamics to symbiotic relationships.
Food Chain and Food Web
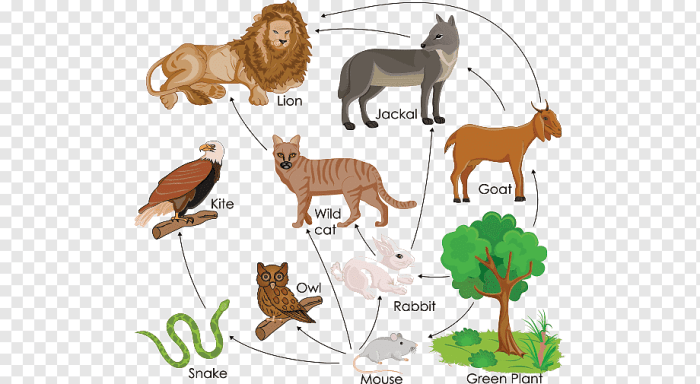
A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass, starting with a producer organism and ending with a top predator. A food web is a more complex representation of the feeding relationships between multiple organisms in an ecosystem, where multiple food chains are interconnected.
Example Food Chain:Grass → Zebra → Lion
Example Food Web:
- Grass → Zebra → Lion
- Grass → Wildebeest → Lion
- Zebra → Hyena
- Lion → Vulture
Trophic Levels, Lion king food web worksheet answers
Trophic levels are hierarchical levels in a food web that categorize organisms based on their feeding habits.
Trophic Levels in the Lion King Food Web:
- Producers:Plants (grass, trees)
- Primary Consumers:Herbivores (zebra, wildebeest)
- Secondary Consumers:Carnivores (lion, hyena)
- Tertiary Consumers:Top predators (lion)
- Decomposers:Vultures, bacteria
Energy Flow
Energy flows through a food web as organisms consume and are consumed. Producers capture energy from the sun through photosynthesis, and this energy is passed up the food chain to consumers.
Role of Organisms in Energy Flow:
- Producers:Capture energy from the sun
- Consumers:Obtain energy by consuming other organisms
- Decomposers:Break down dead organisms and recycle nutrients
Interactions Between Organisms
Organisms in a food web interact in various ways, including:
Predator-Prey Relationships:Lion (predator) preys on zebra (prey).
Competition:Lions and hyenas compete for prey (zebra, wildebeest).
Mutualism:Vultures benefit from eating carcasses left by lions, while lions benefit from vultures removing potential disease sources.
Food Web Dynamics
Changes in one part of a food web can have ripple effects on other parts.
Potential Impacts of Human Activities:
- Habitat loss:Reduced plant growth affects herbivore populations, impacting predators.
- Overhunting:Depletion of prey species can disrupt the balance of the food web.
- Pollution:Chemicals can accumulate in organisms, affecting their health and availability as food sources.
Essential FAQs: Lion King Food Web Worksheet Answers
What is a food web?
A food web is a complex network of interconnected food chains that depicts the feeding relationships between multiple species within an ecosystem.
What are the different trophic levels in a food web?
Trophic levels represent the position of an organism in the food web, with producers (plants) at the base, followed by primary consumers (herbivores), secondary consumers (carnivores), and so on.
How does energy flow through a food web?
Energy enters the food web through producers and is transferred to higher trophic levels as organisms consume each other. At each transfer, a significant portion of energy is lost as heat.