Bloodborne pathogens and standard precautions test answers – Delve into the realm of bloodborne pathogens and standard precautions with this comprehensive guide. Our exploration will encompass the modes of transmission, preventive measures, and post-exposure management strategies for these potentially hazardous microorganisms.
We will also shed light on the importance of sharps safety, waste management, and regulatory compliance in ensuring the well-being of healthcare workers and patients alike. Join us as we unravel the intricacies of bloodborne pathogen prevention and control.
Bloodborne Pathogens: Transmission and Prevention: Bloodborne Pathogens And Standard Precautions Test Answers
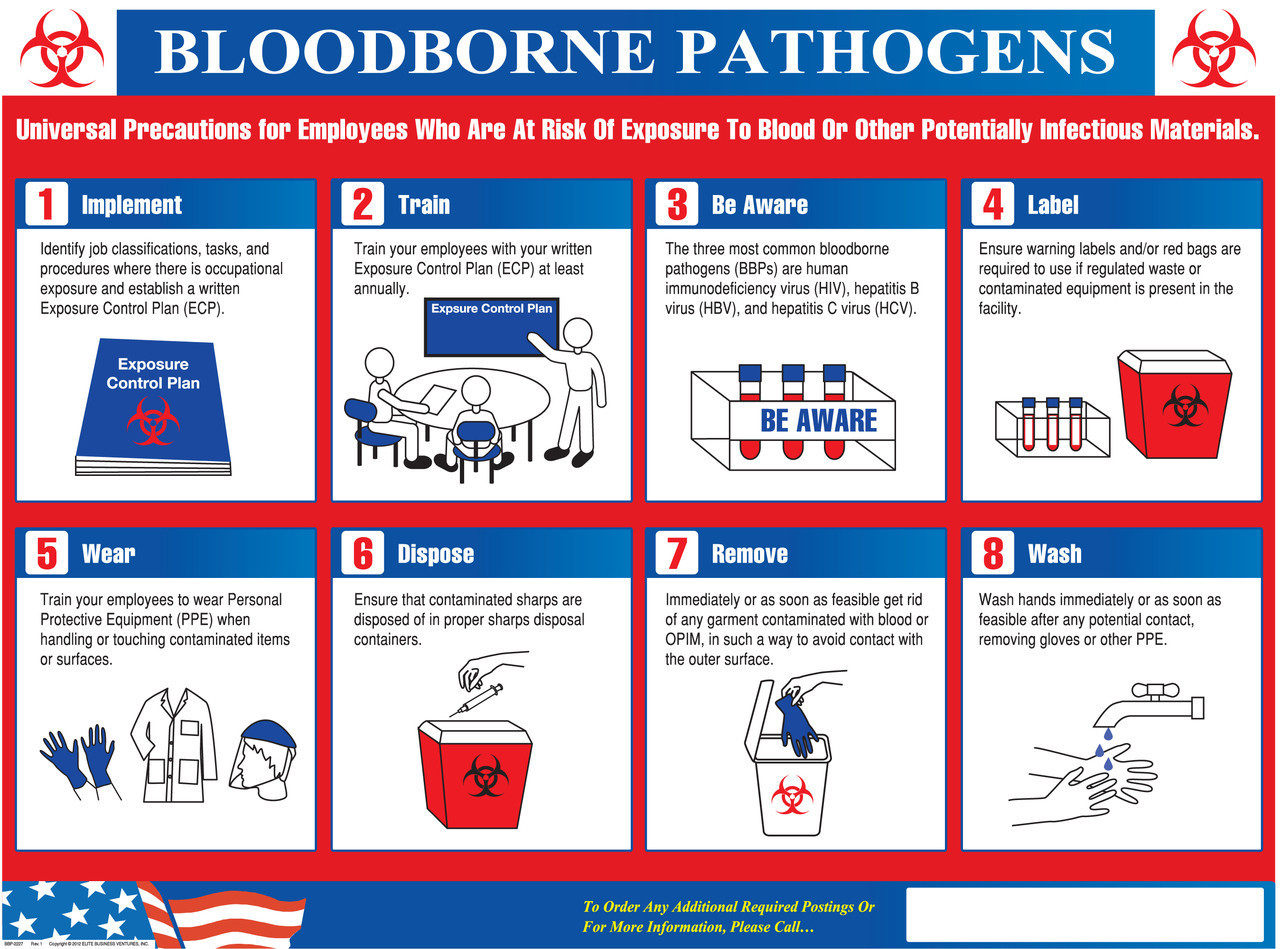
Bloodborne pathogens, such as hepatitis B virus (HBV), hepatitis C virus (HCV), and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), are transmitted through contact with infected blood or other potentially infectious materials. The primary modes of transmission include:
Percutaneous exposure
Contact with sharp objects contaminated with infected blood, such as needles or surgical instruments.
Mucous membrane exposure
Contact with infected blood or body fluids with the eyes, nose, or mouth.
Non-intact skin exposure
Contact with infected blood or body fluids through cuts, abrasions, or open wounds.To prevent exposure to bloodborne pathogens, healthcare facilities implement standard precautions, which are a set of infection control practices that apply to all patients, regardless of their known or suspected infection status.
These precautions include:
Hand hygiene
Washing hands frequently with soap and water or using an alcohol-based hand sanitizer.
Personal protective equipment (PPE)
Wearing gloves, gowns, masks, and eye protection when there is a potential for exposure to blood or body fluids.
Safe handling of sharps
Using sharps containers for disposal and avoiding recapping needles.
Environmental cleaning and disinfection
Cleaning and disinfecting surfaces and equipment that may have come into contact with blood or body fluids.
Exposure Control Plan: Elements and Implementation
An exposure control plan is a written document that Artikels the procedures and policies for preventing and responding to bloodborne pathogen exposures in healthcare settings. Key components of an exposure control plan include:
Exposure determination
Identifying tasks and procedures that pose a risk of exposure to bloodborne pathogens.
Methods of control
Implementing standard precautions and other measures to minimize the risk of exposure.
Post-exposure management
Establishing procedures for reporting, investigating, and managing bloodborne pathogen exposures.
Employee training
Providing education and training to healthcare workers on bloodborne pathogen prevention and exposure control measures.Implementing an exposure control plan involves:
- Developing and implementing written policies and procedures.
- Training healthcare workers on the plan and its requirements.
- Monitoring and evaluating the plan’s effectiveness.
- Revising the plan as needed to ensure its ongoing effectiveness.
Healthcare workers are responsible for adhering to exposure control measures Artikeld in the plan, including:
- Following standard precautions.
- Using PPE appropriately.
- Reporting exposures promptly.
- Participating in training and education programs.
Post-Exposure Management: Reporting, Treatment, and Follow-Up
Following a bloodborne pathogen exposure incident, it is crucial to follow established reporting, treatment, and follow-up procedures.Reporting
- Report the exposure to the supervisor or designated person immediately.
- Complete an exposure report form, providing details of the incident.
- Notify the source patient’s healthcare provider if necessary.
Treatment
Post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP)
Administering antiviral medications to prevent infection, if indicated.
Baseline testing
Testing for HBV, HCV, and HIV to establish a baseline.
Follow-up testing
Testing at regular intervals to monitor for seroconversion.Follow-Up
- Monitor for symptoms of infection.
- Provide counseling and support to the exposed individual.
- Offer HIV testing and counseling to the source patient, if appropriate.
Sharps Safety: Practices and Devices
Sharps safety practices aim to minimize the risk of sharps-related injuries and bloodborne pathogen exposure in healthcare settings. Key principles include:
- Avoid recapping needles.
- Use sharps containers for disposal.
- Implement needleless systems where possible.
- Dispose of sharps immediately after use.
Types of sharps safety devices include:
Needleless IV systems
Systems that allow for medication administration without the use of needles.
Safety-engineered sharps
Sharps with built-in safety features, such as retractable needles or needleless syringes.
Sharps containers
Puncture-resistant containers designed for safe disposal of sharps.Best practices for sharps handling and disposal include:
- Never pass sharps directly from hand to hand.
- Place sharps containers in convenient locations.
- Label sharps containers clearly.
- Dispose of sharps containers according to established protocols.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common modes of transmission for bloodborne pathogens?
Bloodborne pathogens are primarily transmitted through contact with infected blood or other bodily fluids, such as semen, vaginal secretions, and breast milk.
What are the key elements of an exposure control plan?
An exposure control plan Artikels the policies and procedures for preventing and managing exposure to bloodborne pathogens in healthcare settings. It includes measures such as universal precautions, personal protective equipment (PPE), and post-exposure prophylaxis.
What are the responsibilities of healthcare workers in adhering to bloodborne pathogen precautions?
Healthcare workers are responsible for following standard precautions, using PPE appropriately, reporting exposures promptly, and seeking post-exposure prophylaxis if necessary.