As a balloon rubbed against denim gains a charge of, it sparks an intriguing exploration into the realm of electrostatics. This captivating phenomenon, rooted in the fundamental principles of charge transfer, unfolds before our eyes, inviting us to unravel the intricate interplay of electrons and materials.
The journey begins with an examination of electrostatic charge, its nature, and its profound implications for the experiment at hand. We delve into the triboelectric series, a hierarchy of materials that dictates their propensity to gain or lose electrons, setting the stage for the charge separation that occurs when balloon meets denim.
Electrostatic Charge

Electrostatic charge refers to the accumulation of an electrical charge on the surface of an object. It arises from an imbalance between the number of protons and electrons in an object, resulting in a net positive or negative charge. The experiment of rubbing a balloon against denim demonstrates the concept of electrostatic charge.
Materials that can easily gain or lose electrons are called conductors, while those that resist the flow of electrons are called insulators. When a balloon is rubbed against denim, electrons are transferred from the denim to the balloon, causing the balloon to gain a negative charge while the denim acquires a positive charge.
Triboelectric Series
The triboelectric series is a list of materials arranged in order of their tendency to gain or lose electrons when rubbed against each other. Materials higher in the series tend to gain electrons easily, while those lower in the series tend to lose electrons easily.
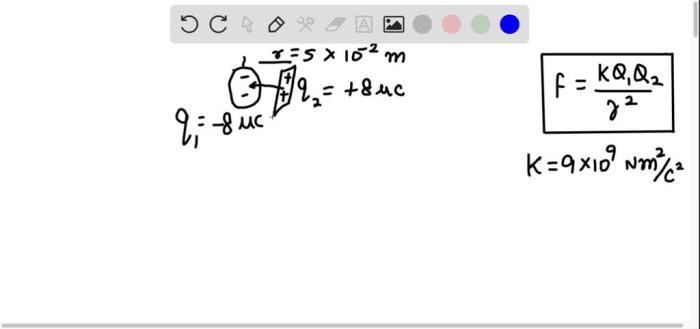
In the experiment, denim is higher in the triboelectric series than the balloon. This means that when the balloon is rubbed against the denim, electrons flow from the denim to the balloon, giving the balloon a negative charge and the denim a positive charge.
The following table shows some common materials and their positions on the triboelectric series:
| Material | Position on Triboelectric Series |
|---|---|
| Human skin | Positive |
| Glass | Positive |
| Rubber | Negative |
| Denim | Negative |
| Teflon | Strongly negative |
Charge Separation
When a balloon is rubbed against denim, electrons move from the denim to the balloon, creating a separation of charge. The balloon becomes negatively charged because it has an excess of electrons, while the denim becomes positively charged because it has a deficit of electrons.
The charge distribution on the balloon and denim can be illustrated as follows:
Balloon:Negative charge on the surface
Denim:Positive charge on the surface
Static Discharge, A balloon rubbed against denim gains a charge of
Static discharge occurs when the accumulated electrostatic charge on an object is released. This can happen through a spark, a shock, or a corona discharge.
For static discharge to occur, there must be a difference in electrical potential between two objects. When the potential difference becomes too great, the air between the objects breaks down and allows the charges to flow, resulting in a discharge.
The experiment of rubbing a balloon against denim can create static discharge. When the balloon is brought close to a grounded object, such as a wall or a person, the potential difference between the balloon and the object becomes large enough to cause a discharge.
This discharge can be seen as a spark or heard as a crackle.
Applications
Electrostatic charging has a wide range of practical applications, including:
- Electrostatic precipitators:These devices use electrostatic charge to remove particulate matter from the air. The particles are charged and then attracted to a collector plate, where they are removed from the air stream.
- Laser printers:Laser printers use electrostatic charge to transfer toner particles to paper. The toner particles are charged and then attracted to the paper, which has been given a opposite charge.
- Electrostatic spray painting:This technique uses electrostatic charge to attract paint particles to the surface being painted. This results in a more even and consistent coating.
FAQ Explained: A Balloon Rubbed Against Denim Gains A Charge Of
What is electrostatic charge?
Electrostatic charge refers to the buildup of electric charge on the surface of an object, resulting from an imbalance of positive and negative charges.
How does the triboelectric series relate to the experiment?
The triboelectric series ranks materials based on their tendency to gain or lose electrons when in contact with another material. This ranking determines the direction of charge transfer in the experiment.
What is charge separation?
Charge separation occurs when electrons move from one material to another, creating a positive charge on one surface and a negative charge on the other.